The brain plans of various scientific research countries around the world are caused by people's high attention to behavior and brain exploration. A recent report by Nature stated that the China Brain Science Institute was officially established in Beijing on March 22, 2018. The Chinese Brain Project Store opened, and Rao Yi of Peking University and Luo Minmin of the NIBS Beijing Institute of Life Sciences jointly headed. This move is also followed by the brain plan of Europe and the United States in 2013, a similar small project in Japan in 2014, and the follow-up of China after 2016 in Korea. The Beijing Municipal Government has funded 180 million yuan, recruiting about 5 researchers from about 5-6 research groups in five years, and hopes that the brain plan will cost about 400 million yuan per year. It is not difficult to see that the study of the brain is an extremely important and difficult task. It has a long way to go and requires researchers in related fields to contribute their talents, insights and diligence. The following is an interpretation and interpretation of relevant articles on the study of learning and memory mechanisms.
TRPM7 is essential for maintaining normal synaptic density and learning and memory at different developmental stages
Under the efforts of the research team of Nashat Abumaria, a researcher at the National Key Laboratory of Medical Neurobiology, Fudan University, the research results were published on the cover of Cell Reports. The impact factor IF was 8.032, given the cover. The value is higher than the impact factor.
The article focuses on a channel enzyme TRPM7, because it is found in many tissues. The focus here is on its function and role in the CNS central nervous system and in non-pathological conditions under physiological conditions. The exact neurons in the hippocampus Knockdown knocked down and found a decrease in synaptic density, but this phenomenon can be rescued by the C-terminal kinase domain. The rescue mechanism may be phosphorylation of the downstream cofilin protein (Cofilin is an actin-binding protein commonly found in eukaryotic cells). The basic function of protein.Cofilin is to bind and depolymerize F-actin in cells; after the mouse knockout knockout, the learning and memory are damaged and the synaptic density and synaptic plasticity are reduced. The adult rat hippocampus is also knockdown. Damage to learning and memory and reduced synaptic density and synaptic plasticity;
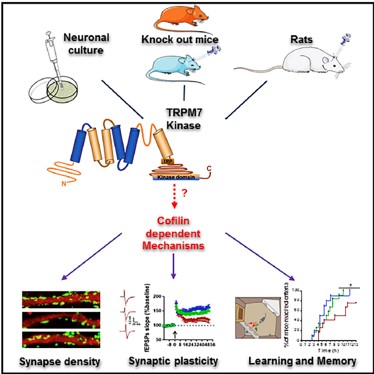
In order to study the effects of this channel enzyme on learning and memory, the mouse and rat models were selected. In order to observe the function of this channel enzyme, Knockdown knockdown (for adult rats) and Knockout knocking were performed. In addition to the two treatments (for postnatal mice), the rescue experiment was performed by injecting the enzyme back into the brain of Knockout knockout mice to observe the effect (for mice, and for the partial region of the enzyme, the kinase Regional), for the main metrics including synaptic density, synaptic plasticity, and learning and memory behavior, the first two methods are more conventional antibody microscopy imaging, in vitro electrophysiological recording, the latter group adopted The Nordic's new Cognition Wall cognitive wall tool in the Netherlands judges learning and memory behavior, which deserves attention. I will talk about it later.
1. In vitro cell level
First, in vitro, at the cellular level, Knockdown knocks down the expression of TRPM7 and looks at the hippocampal neurons. Of course, the expression is reduced after knockout and does not affect the expression of other proteins and does not affect the growth of neurons. The discovery of synaptic density was significantly reduced, and synaptophysin was also significantly reduced!
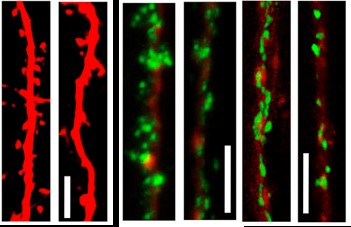
The left side of the figure is the control group, and the right side is the experimental group after knocking down. It can be seen that various important stains show a significant decrease in synaptic density and synaptophysin after knockdown. After the above many knockdown results, what is working, so the rescue experiment was carried out to increase the concentration of magnesium ions and zinc ions. No, even the intracellular concentration of the two was not related to TRPM7. It seems that the non-ion channel is Synaptic density reduction works; later added to the C-terminal kinase region, found that synaptic density is significantly improved!
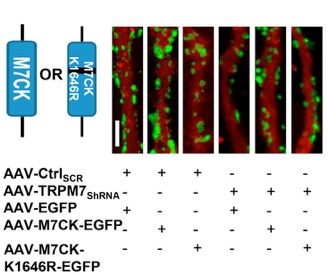
The above six fluorescence maps, the second one is added to the C-terminal kinase region, and the synaptic density is found to be significantly increased, while the third one is the mutation of the C-terminal kinase, which cannot be improved, and its specificity is visible!
2, animal model level
Enter the animal stage of mice and rats!
In mice with specific knockouts, genes in specific regions of the brain knocked out TRPM7 to see the actual individual level, and it was normal to examine some basic behavioral parameters such as motor activity and motivation to explore new objects. The cognitive parameters of the new object recognition, the mice dropped significantly after knocking out. In the learning cognitive experiment, the mice after knockout showed a significant decline in learning ability. Only 40% of the mice learned the cognitive wall experiment, and the learning stage obtained fewer particle rewards. The memory stage made less correct. select. Moreover, the synaptic density in the CA1 region (a region of the hippocampus) also decreased significantly. Moreover, the decrease in presynaptic terminal density and the decrease in post-synaptic field excitatory potential indicate that the synaptic plasticity of the knockout mouse is impaired.
figure 1:
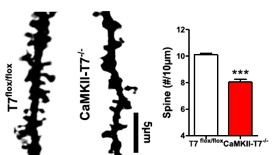
figure 2:
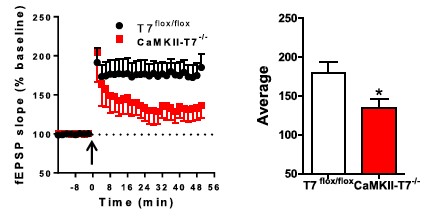
The left side of Figure 1 is black for the synaptic density of the control group, and the black for the right side is the synaptic density of the knockout group, which is significantly reduced! Figure 2 shows the field excitatory postsynaptic potential, black is the long-term potentiation of LTP in the control group, red is the long-term potentiation of LTP in the knockout group, and the prominent plasticity is impaired!
These declines in synaptic density, impaired synaptic plasticity, and behavioral learning are cognitive problems.
Study on Learning Cognitive Behavior Using Cognition Wall Cognitive Wall Tools from Nordos, Netherlands
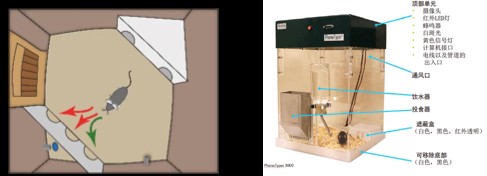
The Cognition Wall cognitive wall tool includes the EthoVision software system and the PhenoTyper mouse home box and three-hole cognitive wall. Animals enter from a specific entrance (the above picture shows the green entrance), the software automatically gives food rewards (the blue particle display above). The experiment is automatic, no human intervention, the software automatically controls the hardware and automatically records the data and automatically analyze data.
The experiment is as follows:
- One week before the experiment, mice were housed in standard cages in single cages;
- The mice were placed in the mouse home box 11 hours before the start of the experiment, and they were adapted to the environment, that is, the mice were placed at about 8:30 pm, and the water was restricted to eat;
- Put 10 foods in this adaptation stage so that the mice can find where the food is given.
- Put it into the cognitive wall at 7:30 in the morning and start the experiment at 8:00 in the morning.
- In this process, the mouse needs to continuously enter the left hole 5 times, and the software automatically controls the hardware to give a grain of food (ie, the green hole in the above figure).
Tip: The mouse rhythm of this article is to turn off the lights at 8:00 pm until 8:00 am the next day, and the red dim light is used as the evening time, ie light phase 8:00pm-8:00am dark phase 8:00am-8 :00pm where dark phase is the experimental time period.
The following illustration shows the experimental results:
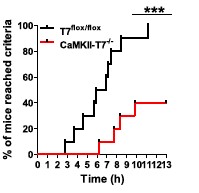
From the results, it can be seen that only 40% of the mice with the red line of gene knockout learned the cognitive wall! The control group learned all! The contrast is obvious!
In the memory test phase after one day, the mice were returned to the home box with the cognitive wall, and the proportion of the mice making the correct selection (ie, entering from the left hole) was calculated in the one-hour test.
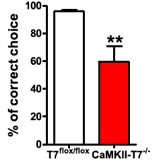
As can be seen from the results, the proportion of mice with the red line of knockout was correctly selected to be significantly lower than that of the control group.
In order to ensure that there is no problem with the food reward device, the experimenter also manually counts the number of food rewards each mouse receives during the learning process, since the number of food rewards is related to the learning ability of the mouse.
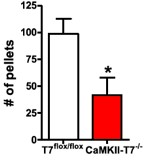
Obviously, the number of food rewards for knockout mice was lower than that of the control group, and the learning ability was significantly weaker than that of the control group.
Not finished! The C-terminal kinase virus was injected into the mouse model for rescue experiments, the control group, the kinase group, and the mutant kinase group. After one month, the behavioral test was performed and further analysis was performed. The cognitive parameters of the new object recognition, the control group and the kinase group. Both were significantly higher than the mutant kinase group. In the learning cognitive experiment, both the control group and the kinase group were significantly faster to learn, and the memory test made more correct choices. Of course, synaptic density and synaptic plasticity are higher than the mutation group.
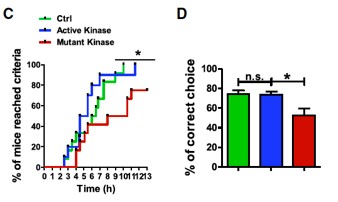
This corresponds to the initial cell experiment, which validated the key role of C-terminal kinases in learning and memory on animal models and behavioral experiments.
Of course, in the rat model, in the specific knockdown rats, after determining the knockdown of its expression, there is no difference in the same basic behavioral parameters, and then the learning and memory ability of the rat is determined, and the T-maze space learning experiment (after knocking down) The proportion of making the right choices is significantly reduced.) The short-term recognition memory (the process in which past experiences or memorized things can still be confirmed and recognized when presented in front of them) is also damaged, the background memory is also impaired, and of course the synaptic density. Both synaptic plasticity decreased significantly.
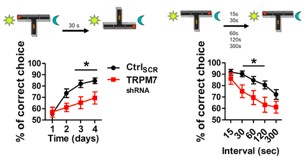
On the last topic, the literature reports that some of the functions involved in cofilin are similar to those after TRPM7 knockout. It is hypothesized that TRPM7 may participate in the downstream mechanism by means of cofilin at the cognitive level, and that cofilin phosphorylation (inhibition) is significantly reduced after knockout. The phosphorylation of the cofilin in the kinase group was restored and it was verified that the two were directly bound.
Of course, the downstream research is relatively simple, biased towards the phenomenon of the phenomenon, and can not directly study with learning and memory. In addition, the function of the kinase is to further elucidate the mechanism of synaptic density through presynaptic and synaptic regulation.
Follow the WeChat QR code below for more product information and news!

references:
Liu YQ#,Chen C#,Liu YL#,Li W, Wang ZH,Sun QF,Zhou H,Chen XJ,Yu YC,Wang Y,Nashat Abumaria*. (2018) TRPM7 Is Required for Normal Synapse Density, Learning, and Memory at Different Developmental Stages .Cell Reports.23(12):3480–3491
Card Recognition Time Attendance
Shenzhen Bio Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.hfsecuritytech.com