A radiotherapy method developed by biological X-ray irradiation in recent years has the advantages of high safety, convenient use, and can be used in an ordinary laboratory environment. In the field of scientific research, it is often used to replace the traditional gamma source irradiation.
American Cellrad biological X-ray irradiator has 130KV X-ray energy, which can be used to irradiate cells or small animals for stem cells (bone marrow transplantation and differentiation, feeder cell preparation, cell mutagenesis, etc.), DNA damage, Cell Biotechnology research such as cycle, cell culture, blood product irradiation, tumor, signal transduction, immunity, gene therapy, radiobiology, drug development.
DNA stores the genetic information on which organisms depend for survival and reproduction, so maintaining the integrity of DNA molecules is critical to the cell. The external environment and the factors inside the organism often lead to damage or change of DNA molecules, and it is different from RNA and protein synthesis in cells. Generally, there is only one DNA in a prokaryotic cell, in eukaryotic diploid cells. There is only one pair of the same DNA. If the damage of DNA or the change of genetic information cannot be corrected, the body cells may affect their function or survival, and the germ cells may affect the offspring. Therefore, the ability of biological cells to repair DNA damage during evolution is important, and it is also where biological energy maintains genetic stability.
DNA damage caused by ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation damages DNA with direct and indirect effects. The direct effect is that DNA directly absorbs ray energy and is damaged. The indirect effect means that other molecules (mainly water molecules) around the DNA absorb ray energy to produce highly reactive free radicals. Damage to DNA. Ionizing radiation can cause multiple changes in DNA molecules: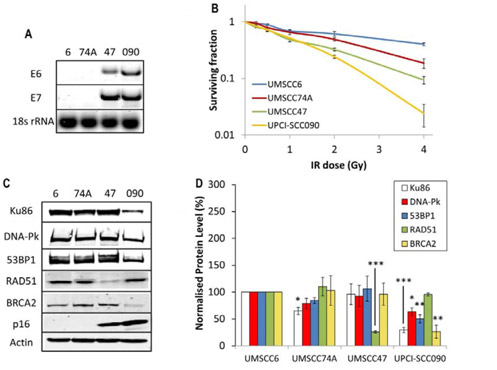 For example, the misregulation of DNA damage repair pathway in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma contributes to cell radiosensitivity
For example, the misregulation of DNA damage repair pathway in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma contributes to cell radiosensitivity
(B) Analysis of clone formation survival of OPSCC cells after treatment with increasing doses of X-ray irradiation (0-4 Gy). Shown is the surviving fraction with standard error from at least three independent experiments. The survival score of 2 Gy(SF2) was compared by one-way analysis of variance. The results showed that p <0.01 (UMSCC6 and UMSCC47), p <0.005 (UMSCC6 and UPCI-SCC090), p <0.02 (UMSCC74A and UMSCC47), p <0.002 ( UMSCC74A and UPCI-SCC090).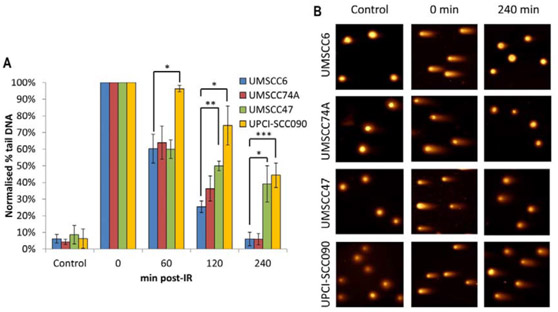 Figure 2: Comparative efficiency of DNA DSB repair in HPV-negative and HPV-positive OPSCC cells.
Figure 2: Comparative efficiency of DNA DSB repair in HPV-negative and HPV-positive OPSCC cells.
(A) Irradiated cells (4 Gy) and DNA DSB were measured at different time points after IR by neutral single cell gel electrophoresis. The % tail DNA was shown to have a standard deviation from at least three independent experiments, normalized to the level immediately observed after IR (0 minutes), which was set to 100%. *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, analyzed by a sample t-test of normalized % tail DNA values ​​in each cell of UMSCC6 cells at each specific time point.
(B) Representative images of OPSCC cells visualized by a neutral comet assay demonstrating HPV-positive defect repair of DNA DSB in HPV-negative OPSCC cells.
Source: Misregulation of DNA damage repair pathways in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma contributes to cellular radiosensitivity (Catherine M. Nickson1, Parisa Moori1, Rachel J. Carter1, Carlos P. Rubbi1, Jason L. Parsons1)
American Cellrad biological X-ray irradiator has 130KV X-ray energy, which can be used to irradiate cells or small animals for stem cells (bone marrow transplantation and differentiation, feeder cell preparation, cell mutagenesis, etc.), DNA damage, Cell Biotechnology research such as cycle, cell culture, blood product irradiation, tumor, signal transduction, immunity, gene therapy, radiobiology, drug development.
DNA stores the genetic information on which organisms depend for survival and reproduction, so maintaining the integrity of DNA molecules is critical to the cell. The external environment and the factors inside the organism often lead to damage or change of DNA molecules, and it is different from RNA and protein synthesis in cells. Generally, there is only one DNA in a prokaryotic cell, in eukaryotic diploid cells. There is only one pair of the same DNA. If the damage of DNA or the change of genetic information cannot be corrected, the body cells may affect their function or survival, and the germ cells may affect the offspring. Therefore, the ability of biological cells to repair DNA damage during evolution is important, and it is also where biological energy maintains genetic stability.
DNA damage caused by ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation damages DNA with direct and indirect effects. The direct effect is that DNA directly absorbs ray energy and is damaged. The indirect effect means that other molecules (mainly water molecules) around the DNA absorb ray energy to produce highly reactive free radicals. Damage to DNA. Ionizing radiation can cause multiple changes in DNA molecules:

(B) Analysis of clone formation survival of OPSCC cells after treatment with increasing doses of X-ray irradiation (0-4 Gy). Shown is the surviving fraction with standard error from at least three independent experiments. The survival score of 2 Gy(SF2) was compared by one-way analysis of variance. The results showed that p <0.01 (UMSCC6 and UMSCC47), p <0.005 (UMSCC6 and UPCI-SCC090), p <0.02 (UMSCC74A and UMSCC47), p <0.002 ( UMSCC74A and UPCI-SCC090).

(A) Irradiated cells (4 Gy) and DNA DSB were measured at different time points after IR by neutral single cell gel electrophoresis. The % tail DNA was shown to have a standard deviation from at least three independent experiments, normalized to the level immediately observed after IR (0 minutes), which was set to 100%. *p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.005, analyzed by a sample t-test of normalized % tail DNA values ​​in each cell of UMSCC6 cells at each specific time point.
(B) Representative images of OPSCC cells visualized by a neutral comet assay demonstrating HPV-positive defect repair of DNA DSB in HPV-negative OPSCC cells.
Source: Misregulation of DNA damage repair pathways in HPV-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma contributes to cellular radiosensitivity (Catherine M. Nickson1, Parisa Moori1, Rachel J. Carter1, Carlos P. Rubbi1, Jason L. Parsons1)
Food Processing Nitrile Gloves
Food Processing Nitrile Gloves,Food Gloves Nitrile,Disposable Industry Gloves,Textured Finger Free Latex Gloves
Puyang Linshi Medical Supplies Co., Ltd. , https://www.linshihealths.com