Summary of the latest progress in breast cancer treatment in 2017
January 9, 2018 Source: Sina medicine Author: unique eye medicine
Window._bd_share_config={ "common":{ "bdSnsKey":{ },"bdText":"","bdMini":"2","bdMiniList":false,"bdPic":"","bdStyle":" 0","bdSize":"16"},"share":{ }};with(document)0[(getElementsByTagName('head')[0]||body).appendChild(createElement('script')) .src='http://bdimg.share.baidu.com/static/api/js/share.js?v=89860593.js?cdnversion='+~(-new Date()/36e5)];From the clinical study data released in 2017, optimized anti-HER2 therapy is beneficial for patients with early high-risk HER2-positive breast cancer; capecitabine is beneficial for breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant therapy. For advanced breast cancer, endocrine therapy combined with a cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK4/6) inhibitor or olaparib may be a clinical priority.
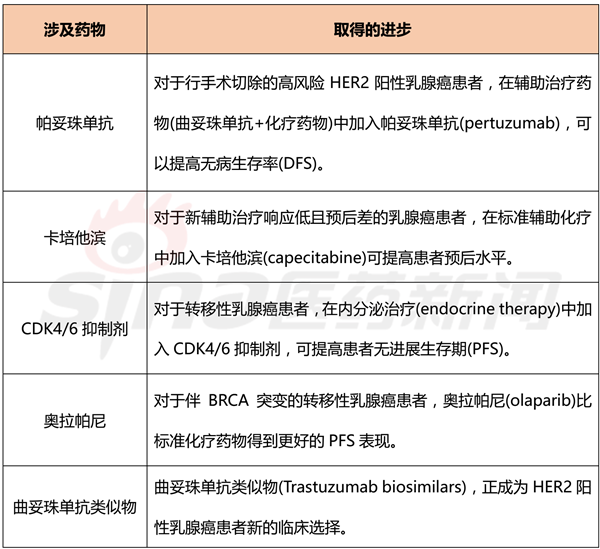
Table 1 Key advances in breast cancer treatment in 2017
background
In the past few years, cancer treatment research has made great progress. Before a new treatment plan is finally applied to practice, the researchers also need a complete clinical trial evaluation. In 2017, in the field of breast cancer, several clinical trial results of much attention have been published, and most of them have achieved satisfactory results. On the one hand, the patient's prognosis level is improved, and on the other hand, the patient's treatment cost is lowered.
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy, also known as preoperative chemotherapy, induction chemotherapy, initial therapy, etc., refers to the treatment of systemic chemotherapy before surgery. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy is not a new treatment, but rather is different from adjuvant chemotherapy at the time of systemic treatment.
Neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer began in the 1970s. With the establishment of adjuvant chemotherapy in the treatment of breast cancer, neoadjuvant chemotherapy has begun to be used for inoperable locally advanced breast cancer, and the tumor has been reduced by chemotherapy, thus making it impossible for inoperable patients to obtain surgical treatment, greatly improving these patients. The quality of life, the application of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in this part of the patient has been widely recognized.
The International Committee of Experts reached a consensus in 2008 that the indications for neoadjuvant chemotherapy are patients who are inoperable or have breast-conserving expectations but are too large to breast-contain.
Pertuzumab
Pertuzumab, a HER2 dimerization inhibitor, is the first neoadjuvant drug to accelerate the approval of patients with HER2-positive early breast cancer. Compared with the control group, the addition of pertuzumab in the treatment regimen of trastuzumab plus chemotherapy resulted in a sustained statistically significant increase in pathologic complete response rate (pCR).
In a phase III clinical trial called APHINITY, 4,805 HER2-positive breast cancer patients were enrolled, with a median follow-up of 45.4 months. Pertuzumab was added to the treatment regimen of trastuzumab plus chemotherapy, and the recurrence rate of invasive breast cancer was reduced by 19% compared with placebo (HR 0.81, 95% CI 0.66–1; P = 0.045). In my opinion, this clinical trial is of great significance. First, the neoadjuvant therapy model can be used as an effective platform to accelerate drug approval. Second, pertuzumab significantly improves the prognosis of HER2-positive breast cancer patients.
Capecitabine
For those breast cancer patients who respond poorly to neoadjuvant therapy, the clinical trial CREATE-X offers another option for this group of patients. This clinical trial recruited 910 Asian HER2-negative breast cancer patients who underwent neoadjuvant therapy. Standard treatment has not been cured. The test group used standard chemotherapy drugs + capecitabine, and the control group used standard chemotherapy drugs + placebo. The DFS and overall survival (OS) of the experimental group were improved compared with the control group. In most countries of the world, the adjuvant drug capecitabine has been used clinically. There are a number of similar clinical trials ongoing to evaluate the benefits of other ancillary drugs for patients who respond poorly to neoadjuvant therapy.
CDK4/6 inhibitor
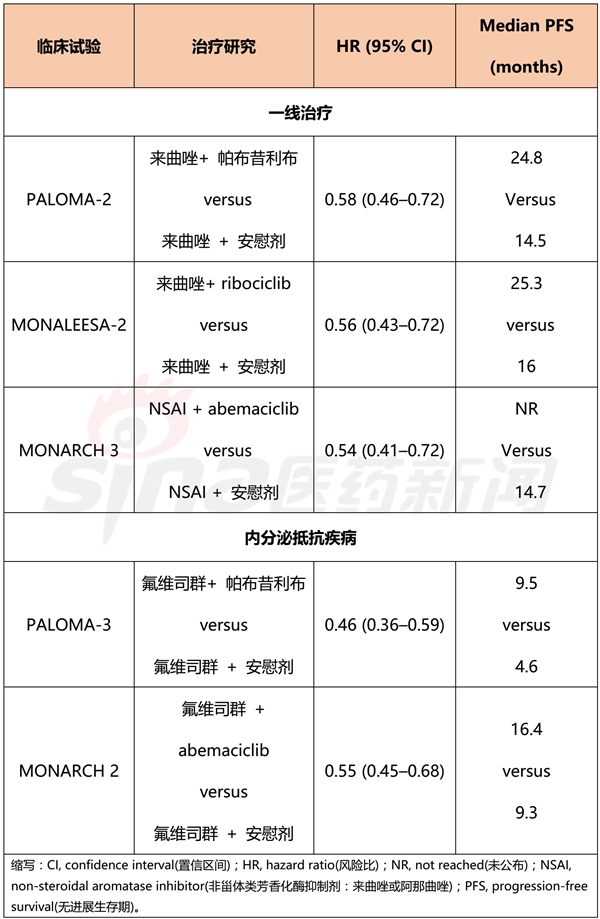
The most important clinical advancement achieved in 2017 occurred in the treatment of advanced breast cancer. In the past few years, third-generation aromatase inhibitors have been first- and second-line treatments for postmenopausal estrogen receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer patients and HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer patients, respectively. Aromatase inhibitors are used in combination with CDK4/6 inhibitors to achieve better therapeutic effects than single agents, which has led to changes in clinical treatment regimens. The clinical trial data of the combination of the CDK4/6 inhibitors palbociclib, ribociclib, abemaciclib and aromatase inhibitors (letrozole, fulvestrant) are shown in Table 2.
The median progression-free survival of the trial group was nearly doubled compared with the placebo group. Although these clinical trials have not yet been published, these trial data are still useful for guiding clinical practice: first, the choice of treatment depends on toxicity or economic factors; second, delaying the use of cytotoxic drugs can help improve patient life. Quality; third, oral medication is more convenient than intravenous injection, reducing the number of hospitalizations.
Table 2 Performance of CDK4/6 inhibitors in clinical trials
PARP inhibitor
For BRCA-positive metastatic breast cancer, PARP inhibitors show good activity and will become a new option for clinical treatment in the coming months. In a phase III clinical trial called OlympiAD, 302 patients with platinum-sensitive HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer with BRCA mutations were enrolled, and olaparib alone was compared with a chemotherapy regimen developed by a physician, Orapa The median progression-free survival of the Ni group was 7 months, which was longer than the control group of 4.2 months, and the toxicity data were in line with expectations. However, the efficacy of PARP inhibitors in patients with platinum tolerance is still controversial.
Conclusion
Despite the great progress in cancer treatment in recent years, metastatic breast cancer and triple-negative breast cancer remain a problem in front of people. Future clinical trials will continue to promote the development of immunotherapy, new target drugs, antibody-drug coupling agents (ADCs), and new cytotoxic drugs to provide more precise therapeutic drugs for various breast cancer treatments and improve clinical benefits.
Safety Pants
Safety Pants, reflective pants, work wear pants, anti cut pants, hi vis safety work wear, rain Reflective Safety Jacket.
We are the manufacturer for more than 20 years. our main products are Safety Work Clothes, Safety Vest , Reflective Safety Jacket, Safety Jacket Reflective, Safety Hoodies , Safety Pants, Safety Parka, Safety Rainwear, Safety Tshirt and etc.
Sample is available now. Sample time 7-10days.




Safety Pants,Reflective Pants,Work Wear Pants,Anti Cut Pants
Suzhou Golden Gamrnet MFG Co.,Ltd , https://www.suzhoumfg.com