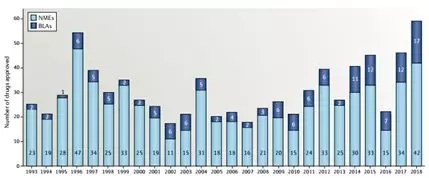
Figure 1. Innovative drugs approved by the FDA in 1993 [2]
The development of antibody therapeutics is so powerful, Xiaobian here is to present two masters, American biologist Gerald Edelman and British biochemist Rodney Porter, who discovered the atomic resolution structure of antibody fragments. , in 1972 was awarded the Nobel Prize (Figure 2) followed GeorgesJ. F. Kohler and Cesar Milstein two scientists as a base Dien, using hybridoma technology to obtain monoclonal antibody (mAb), and then opened the modern antibody The engineering era.


Gerald Maurice Edelman Rodney Porter
Figure 2. Nobel Prize winner in 1972 [3,4]
Monoclonal antibody preparation classic process
The production of monoclonal antibodies is due to the development of hybridoma technology, how is the monoclonal antibody prepared? The following small series gives you a brief summary, as shown in Figure 3:
1 The antigen is injected into the mouse, and after a few weeks, the spleen is taken out and the spleen cells are extracted;
2,3,4 fuses mouse spleen cells with bone marrow cells to produce hybridoma cells, each hybridoma cell produces the same antibody indefinitely, and then uses the antigen/antibody assay to screen hybridoma cells, locking those that produce the expected Antibody cell;
5 cells can also be frozen and stored for later use. This preparation procedure is very useful and can produce a large number of identical specific antibodies relatively easily;
6 re-collecting the hybridoma cells producing the preferred antibody multiple times until the pure line is isolated;
7,8 These cells can also be grown in culture or injected into mice to induce tumors.
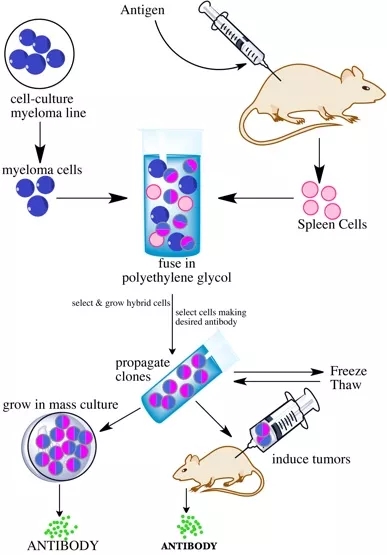
Figure 3. Flow chart of monoclonal antibody production by hybridoma method [5]
Although the above methods have proven to be robust and still widely used to produce monoclonal antibodies, there have been certain limitations in clinical applications.
Image source: soogif
Don't worry, don't worry, Xiaobian will tell you.
Because the early use of B lymphocytes and myeloma cells are from mice, the antibodies produced are derived from the mouse genome (called "mouse antibodies"), which are immunogenic in humans, and the human immune system will use the mouse's mAb. It is recognized as a foreign antigen and produces an immune response (called the HAMA effect) .
Mouse monoclonal antibodies that enter the body are quickly expelled from the circulation, and in some cases allergic reactions can occur. Furthermore, the constant region of the mouse mAb (part of the immune cell recognition portion) is not normally able to interact with receptors on human cells responsible for antibody action. Therefore, mouse monoclonal antibodies rarely produce the desired therapeutic effect on the human body and may be unsafe. Since then, scientists have begun to work toward the direction of "humanization" of mAbs . There is a very simple solution is to use a mouse instead of human B lymphocytes B lymphocytes, but that does not work, because on the one hand, from human hybridoma cells are unstable, human B cells do not produce for Antibodies to human tissues; on the other hand, using some antigens to immunize humans poses safety and ethical issues. [6]
Human and mouse chimeric, humanized and fully human monoclonal antibody development
In order to get a mAb that can be applied to the clinic, scientists are constantly developing antibodies. To date, three key types of antibodies have been developed (Figure 4): human and mouse chimeric antibodies (variable regions of mice + human constant regions), humanized antibodies (mouse CDR regions + human Ig) Scaffold ) and fully human monoclonal antibodies (all human amino acids). [7]
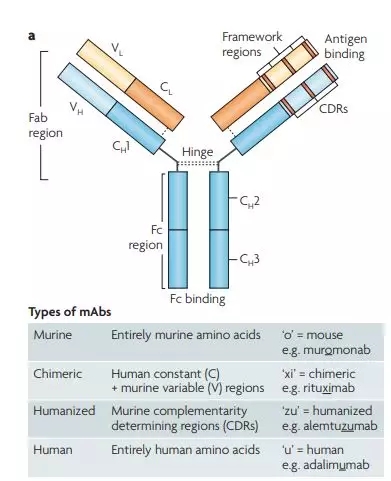
Figure 4. Structure and type of monoclonal antibodies [7]
Rituximab is a chimeric mAb that is clinically used to treat non-Hodgkin's lymphoma . Unfortunately, mouse variable regions are still considered foreign in many cases, which limits the application of chimeric mAbs. [6-7]
Alemtuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody, a new anti-cancer drug for leukemia . The humanized monoclonal antibody has a further exchange between the human sequence and the mouse sequence in the variable region, thereby further reducing immunogenicity. However, the CDRs of the murine monoclonal antibody are present in the humanized monoclonal antibody, and these antibodies usually lose their binding activity. Ideally, the murine residues are reduced in the variable region to produce a functionalized, but immunogenic, humanized monoclonal antibody. [6-7]
The emergence of fully human antibodies : In order to eliminate the immunogenicity of all kinds of monoclonal antibodies mentioned above, great scientists began to engineer mouse B lymphocytes, and all parts of their antibodies were transformed into complete human genes. When these mice are immunized, their immune response will consist entirely of human antibodies . Complete human monoclonal antibodies were obtained from B lymphocytes of these mice in conjunction with standard hybridoma technology. [6-7] Wow! This kind of "four or two dialing" is simply a "smart", is there a wood?
Antibody screening method which can replace hybridoma technology
Having said that, Xiaobian wants to ask the friends, in addition to the above-mentioned use of hybridoma technology to obtain antibodies, is there any other way? Â

Image source: Network
· Phage antibody library display technology - screening of scFv single chain antibody
Phage display is a screening method for replacing hybridomas, similar to hybridomas, starting with B lymphocytes from immunized animals. Main screening process :
1. Extract B-lymphocyte RNA, reverse-transcribe into cDNA, first extract, and use the primers conserved with the antibody gene to amplify the antibody gene by PCR to construct a library;
2. Using genetic engineering to insert a DNA sequence encoding a polypeptide or protein library into the coat protein gene of the phage, and the polypeptide or protein can be expressed on the surface of the phage;
3. The phage is retransformed into the host cell and, after maturation, released from the host;
4. Capturing a phage capable of specifically binding to a target protein using a culture plate immobilized with a target protein;
5. Wash off the phage that has not bound to the target;
6. The phage wash bound to the target is taken off, the host cell is infected, propagated and amplified, and the next round of panning is performed; soluble expression and immunoassay of the antibody fragment in E. coli (including ELISA or flow cytometry) The desired high affinity antibody can be obtained. [8,10]
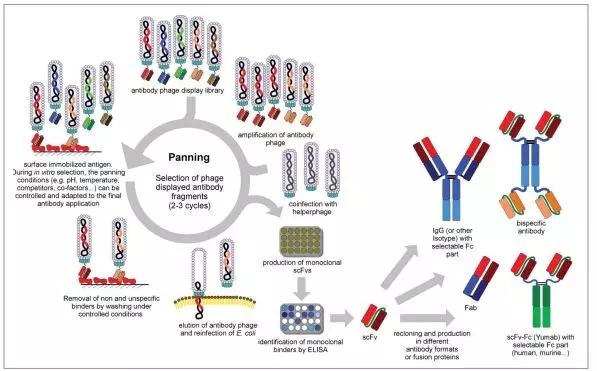
Figure 5. Flow chart of scFv antibody screening by phage antibody library [8]
So, what are the benefits of doing this?
First, not all protein epitopes expressed in the library are useful, so that epitopes of interest can be screened to ensure optimal drug activity;
Second, in vitro experiments can be used to screen both human and non-human targets , which saves time in preclinical testing.
Of course, in vitro screening methods include cDNA display technology for in vitro screening of single domain antibodies (VHH) , ribosome display technology for screening high affinity antibody scFv fragments , peripheral blood antigen-specific B lymphocyte sequencing and affinity determination [1] , Xiaobian is not detailed here.
· Swift and reliable drug screening  (pharmaceutical screening)
After the above in vitro screening, we can get a series of antibody clones with binding activity, then which of these antibody clones is the best?
At this time, we need to further analyze the affinity of these antibodies in vitro, various in vitro activity tests (ADCC, CDC, etc.) and physical and chemical properties analysis, and select a good effect antibody.
Of course, there is an effective way to replace these in vitro activity tests, then directly use the immunological checkpoints to establish a tumor model. Humanized mice are screened for antibodies at the initial stage to obtain the best molecules in vivo! As shown in Figure 6, the CMC Phase G antibody was tested in vivo at different doses (target mouse + MC38 intestinal cancer cell line) and still had a better therapeutic response. In this way, you can get an excellent human antibody candidate drug through the in vivo drug effect, can you fly away and have wood? !
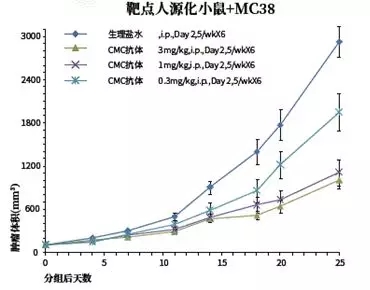
Figure 6. In vivo validation of CMC phase antibodies (Source: Biographs)
Ok, today Xiaobian is here for everyone. One hundred Orsay Figure antibody drug R & D service platform, with a highly efficient method of immunization intact antibody pilot screening process, the antibody can be screened using the in vivo efficacy of various targets humanized mouse; platform can also be engineered antibody , in vitro activity test and physical and chemical properties analysis. If you have any questions, please leave a message below, Xiaobian will reply in time~
references
[1] Roland Kontermann, Stefan Dübel. Antibody Engineering. Methods and Protocols hird Edition.2018.
[2] Asher Mullard.2018 FDA drug approvals. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 18, 85–89
[3]https://baike.baidu.com/item/Gerald Edelman/9559195?fr=aladdin
[4]https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rodney_R._Porter
[5https://cellbiology.med.unsw.edu.au/cellbiology/index.php/file:Preparation_of_mAbs.jpg
[6https://cellbiology.med.unsw.edu.au/cellbiology/index.php/Group_7_Project_-_Monoclonal_Antibodies#cite_note-hansel-15
[7] Hansel, Trevor T. et al. The safety and side effects of monoclonal antibodies. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2010, 9 (4), 325-38 DOI: 10.1038/nrd3003.
[8] Frenzel A, Schirrmann T, Hust M Phage display-derived human antibodies in clinical developpment and therapy. MAbs. 2016 Oct;8(7):1177-1194. Epub 2016 Jul14.
[9https://
[10]https://wenku.baidu.com/view/da12be2d0722192e4536f615.html
Fresh Half Shell Mussel Meat,Half Shell Mussel Meat,Frozen Cooked Mussel Meat,Frozen Mussel
Shengsi Xiangyuan Aquatic Products Co.,Ltd., , https://www.xiangyuan-aquatic.com