Imported French lens
Mould Die-casting Eight edge type Revolving arm
Each LED can be replaced individually, which guarantees maximum economy.
Configuring lightweight balance arm suspension system ,six groups universal joint linkage ,mobile, lightweight positioning and stablibity .A 360°all-round design ,can meet the need for surgery in different heights and angles.
Color temperature constant, soft, very close to the natural sun light.
The use of liquid crystal display button control, to meet the needs of the medical staff of different patients with the brightness of the operation.
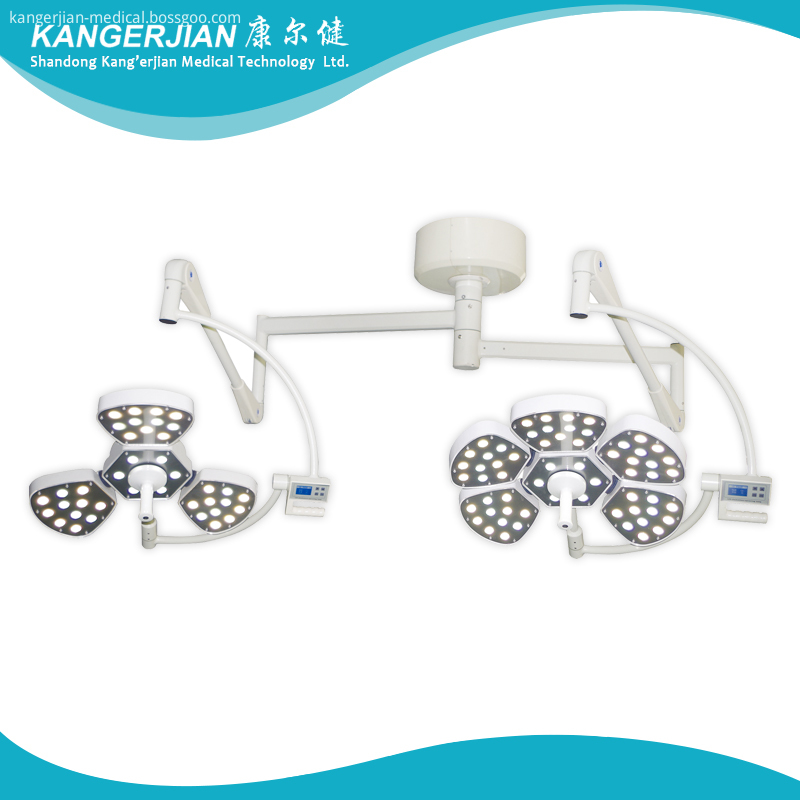

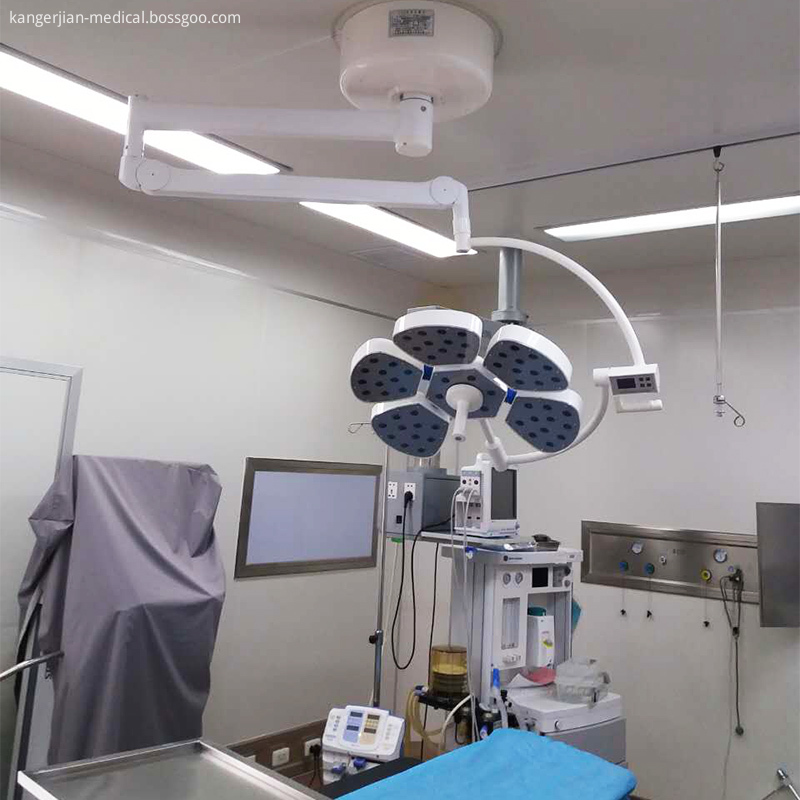
Flower Type Operating Light,Operating Room Lights,Petal Led Surgical Lights,Petal Type Led Surgical Lights
Shandong Kang'erjian Medical Technology Ltd. , http://www.kangerjian-medical.com