The anti-frozen and disaster-relief technical measures of flowers and seedlings---In order to effectively reduce the losses caused to the flowers and seedlings by disasters, in recent days, the provincial flower nursery stock experts proposed antifreeze disaster relief technical measures.
Insulation
In the breeding of seedlings, potted flowers and some annual sales of flowers, precious flowers and green seedlings, all those who can enter the shed to do well into the shed insulation work, timely coverage of the shed film, to prevent cold air intrusion, and should be timely warming fill light . For thermophilic flowers and seedlings native to tropical and subtropical regions, the temperature should be maintained above 12°C. Other flowers and seedlings should be maintained at about 8°C, and the lowest should not be less than 5°C.
Strengthen field management
Timely cover and heat with plastic film or rice straw, chaff, etc.; strengthen field management, drain water in time; remove frost on the plants in time (sway lightly, knock lightly with soft bamboo shoots, but not shoot), and carry out壅蔸 earth.
Trimming
For plants with lighter freezing damage, strictly control the "Ning shallow not deep" light pruning to clear the plants, in order to facilitate bud germination. Heavier victims should be deeply trimmed or heavy trimmed. The frozen parts are cut in time to promote the sprouting of new shoots; after thawing, the shallow cultivating grasses in early spring are combined with topdressing available nitrogen fertilizer, and appropriate application of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers, so that the plants can quickly restore their vitality and improve their resistance to cold and lodging. Ability to promote sprouting and shoot growth. If the permafrost depth is deep, extra-root fertilizer may also be applied with 1% urea + 0.2% potassium dihydrogen phosphate. Freeze injury brings some wounds to the plants. Shallow plough fertilization should be carried out in time.
Another news reporter Song Haifeng reported: In recent days, the provincial tea production experts reminded the majority of tea farmers that after the tea tree is frozen, not only its physiological function is damaged, but also its annual output is affected. It also leads to bald twigs or dead plants. The following measures should be taken to provide care.
Interline coverage, smoke evacuation
Available firewood, straw, turf, leaves, sawmilling ash, glutinous rice, rice husks, rice straw, etc., are used to cover tea gardens before soil freezing. About 1,500 to 2,000 kilograms of grass need to be planted per acre. Straw, weeds, and pruned tea trees can be used for grass cultivation. Branches, etc.; When the temperature dropped to about 2 °C, according to the wind direction, terrain, area set pile ignition, both against late frost and accumulation of fat.
Covering frost and strengthening fertilizer management
For young tea trees, shade can be used to cover the canopy before the low-temperature cold wave arrives. Plastic film, straw, or weeds can also be covered with the shade net; or straw can be directly covered with tea straw; and fertilizer management can be strengthened. Base fertilizer; apply organic fertilizer or NPK fertilizer to increase soil temperature and soil fertility; for tea plants with less severe freezing damage and with good picking surface, do not prune in shallow depth, try to keep picking surface. For those who suffer heavy damage, deep pruning or heavy pruning should be performed.
Shallow fertilization and cultivation of tree crown
After thawing, timely cultivating grasses in shallow early spring, if the depth of permafrost is deep, 1% urea can also be used for extra-root dressing; after the spring tea germination period occurs, after the pruning, the foliar fertilizer should be sprayed at the same time; Frosted tea trees, due to frostbite on the upper leaves, may delay the extraction time of spring tea. Therefore, one large leaf should be left for spring tea picking, and summer and autumn teas are picked as usual. This will not only help improve the canopy, but also use high-grade premium teas to reduce losses caused by freezing damage.
Melting point 280 °C (subl.)(lit.)
Boiling point 246.7°C (rough estimate)
density 1.33
refractive index 1.4260 (estimate)
storage temp. Store at RT.
solubility H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless
form Solid
Water Solubility 895 g/L (20 ºC)
Stability: Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizing agents.
Insulation
In the breeding of seedlings, potted flowers and some annual sales of flowers, precious flowers and green seedlings, all those who can enter the shed to do well into the shed insulation work, timely coverage of the shed film, to prevent cold air intrusion, and should be timely warming fill light . For thermophilic flowers and seedlings native to tropical and subtropical regions, the temperature should be maintained above 12°C. Other flowers and seedlings should be maintained at about 8°C, and the lowest should not be less than 5°C.
Strengthen field management
Timely cover and heat with plastic film or rice straw, chaff, etc.; strengthen field management, drain water in time; remove frost on the plants in time (sway lightly, knock lightly with soft bamboo shoots, but not shoot), and carry out壅蔸 earth.
Trimming
For plants with lighter freezing damage, strictly control the "Ning shallow not deep" light pruning to clear the plants, in order to facilitate bud germination. Heavier victims should be deeply trimmed or heavy trimmed. The frozen parts are cut in time to promote the sprouting of new shoots; after thawing, the shallow cultivating grasses in early spring are combined with topdressing available nitrogen fertilizer, and appropriate application of phosphorus and potassium fertilizers, so that the plants can quickly restore their vitality and improve their resistance to cold and lodging. Ability to promote sprouting and shoot growth. If the permafrost depth is deep, extra-root fertilizer may also be applied with 1% urea + 0.2% potassium dihydrogen phosphate. Freeze injury brings some wounds to the plants. Shallow plough fertilization should be carried out in time.
Another news reporter Song Haifeng reported: In recent days, the provincial tea production experts reminded the majority of tea farmers that after the tea tree is frozen, not only its physiological function is damaged, but also its annual output is affected. It also leads to bald twigs or dead plants. The following measures should be taken to provide care.
Interline coverage, smoke evacuation
Available firewood, straw, turf, leaves, sawmilling ash, glutinous rice, rice husks, rice straw, etc., are used to cover tea gardens before soil freezing. About 1,500 to 2,000 kilograms of grass need to be planted per acre. Straw, weeds, and pruned tea trees can be used for grass cultivation. Branches, etc.; When the temperature dropped to about 2 °C, according to the wind direction, terrain, area set pile ignition, both against late frost and accumulation of fat.
Covering frost and strengthening fertilizer management
For young tea trees, shade can be used to cover the canopy before the low-temperature cold wave arrives. Plastic film, straw, or weeds can also be covered with the shade net; or straw can be directly covered with tea straw; and fertilizer management can be strengthened. Base fertilizer; apply organic fertilizer or NPK fertilizer to increase soil temperature and soil fertility; for tea plants with less severe freezing damage and with good picking surface, do not prune in shallow depth, try to keep picking surface. For those who suffer heavy damage, deep pruning or heavy pruning should be performed.
Shallow fertilization and cultivation of tree crown
After thawing, timely cultivating grasses in shallow early spring, if the depth of permafrost is deep, 1% urea can also be used for extra-root dressing; after the spring tea germination period occurs, after the pruning, the foliar fertilizer should be sprayed at the same time; Frosted tea trees, due to frostbite on the upper leaves, may delay the extraction time of spring tea. Therefore, one large leaf should be left for spring tea picking, and summer and autumn teas are picked as usual. This will not only help improve the canopy, but also use high-grade premium teas to reduce losses caused by freezing damage.
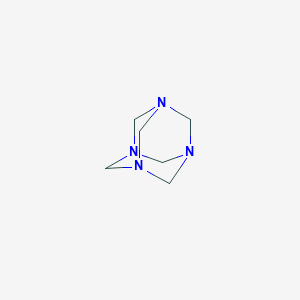
Hexamethylenetetramine Basic Information
CAS: 100-97-0
MF: C6H12N4
MW: 140.19
EINECS: 202-905-8
Mol File: 100-97-0.mol
Hexamethylenetetramine Structure
Melting point 280 °C (subl.)(lit.)
Boiling point 246.7°C (rough estimate)
density 1.33
refractive index 1.4260 (estimate)
storage temp. Store at RT.
solubility H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless
form Solid
Water Solubility 895 g/L (20 ºC)
Stability: Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizing agents.
methenamine,methenamine hippurate,methenamine silver stain,methenamine mandelate,methenamine 1 gram,methenamine tablets
ShanDong YingLang Chemical Co.,LTD , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com