Microelement fertilizers are mainly inorganic salts or oxides. Some minerals and metallurgical by-products or waste materials can often be used as raw materials for microelement fertilizers. The production method is the same as that of inorganic chemical products.
Due to the small amount of application per unit area, it must be diluted with a large amount of inert substances before application. Uneven application will poison some crops. Microelement fertilizers often need to be mixed into macro fertilizers and applied together, usually in two ways: one is to mix them in the production of macro granular fertilizers. This method is more convenient and economical, and does not produce uneven nutrients. The disadvantage is that it is less flexible and difficult to meet the various requirements of the market; the other is to coat the surface of the macro-granular fertilizer with the trace element fertilizer powder. This kind of operation can be carried out in the secondary processing plant, which can meet the needs of the market at any time.
There are two ways to apply trace element fertilizers: soil application and foliar spraying.
Soil fertilization: In addition to chemical fertilizers (such as borax, zinc sulfate, manganese sulfate, etc.), the commonly used micro-fertilizers also include glass fertilizer, slag or scraps, which are usually used as base fertilizer or seed fertilizer. The application method is as follows: before sowing, combine with soil preparation and apply it into the soil, or mix it with nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium and other chemical fertilizers, and apply it uniformly. The application amount should be determined according to the types of crops and micro-fertilizers, and generally should not be too large.
Extra-root topdressing: mix soluble micro-fertilizer into a certain concentration of aqueous solution, and spray the crop stems and leaves. The advantage of this method is to avoid the harm caused by uneven fertilizer in the soil, and it can also be sprayed multiple times according to specific needs at different development stages of the crop to improve fertilizer efficiency.
Disclaimer: Some articles on this website are transferred from the Internet. If the legal rights of a third party are involved, please inform this website for processing. phone
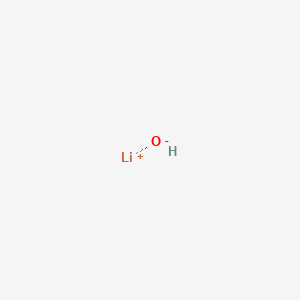
Lithium Hydroxide CAS No.1310-65-2
Lithium Hydroxide Basic Information
CAS: 1310-65-2
MF: LiOH
MW: 23.95
EINECS: 215-183-4
Mol File: 1310-65-2.mol
Lithium Hydroxide Structure
Melting point 462 °C
Boiling point 925°C
density 1.43
storage temp. Store at R.T.
solubility water: soluble71g/L at 20°C
form Solid
Specific Gravity 2.54
color White to light yellow
Stability: Stable. Incompatible with moisture. strong acids, carbon dioxide.
Uses of Lithium Hydroxide
Used in the production of lithium salts and lithium-based greases, electrolytes for alkaline batteries, lithium bromide refrigerator absorption fluids, etc.
Lithium Hydroxide,Lithium Hydroxide Monohydrate,Lithium Hydroxide Formula,Lithium Hydroxide Uses,Lithium Hydroxide Price
Shandong YingLang Chemical Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com