On September 25th, the international academic journal Advanced Materials published the collaborative research results of Liang Gaolin, a professor at the School of Chemistry and Materials Science, University of Science and Technology of China, and Nanjing Medical University. The title of the article is Immune Responsive Release of Tacrolimus to Overcome Organ Transplant. Rejection. This article reports a strategy for the release of tacrolimus from an immune response and has made new advances in overcoming liver transplant rejection studies (Adv. Mater. 2018, 201805018).
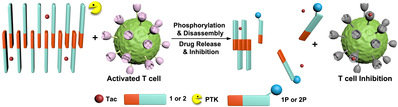
Transplant rejection is the biggest problem facing organ transplantation. Clinically, the method of overcoming transplant rejection is to directly take an immunosuppressive agent (for example, tacrolimus) after the patient has finished surgery to inhibit T cell activation caused by organ transplantation. However, direct administration of large doses of immunosuppressive agents may cause serious side effects to the patient. Studies have shown that activated T cells express high levels of protein tyrosine kinase (PTK), whereas in the large family of protein tyrosine kinases, lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinases (Lck) are found during liver transplantation. Highest expression and secretion to the outside of the cell. Lck has a specific phosphorylation substrate Glu-Tyr. Based on this feature, Liang Gaolin's group designed two hydrogels, Nap-Phe-Phe-Glu-Tyr-OH (1) and Nap-D-Phe-D-Phe-Glu-Tyr-OH (2). He komos. They worked with the liver transplant specialist of Nanjing Medical University, the Wang Xuehao team of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, and the Wang Fuqiang team of the analysis center to apply the hydrogel wrapped in the drug to the liver graft surface. When transplant rejection occurs, activated T cells release Lck, and Glu-Tyr of Lck phosphorylated hydrogel causes degumming to release tacrolimus to inhibit activated T cells (see figure below). Rat liver transplantation experiments showed that rats who received oral tacrolimus on a clinical basis survived an average of 13 days, whereas rats who received a tacrolimus with a hydrogel "smart" immune response survived an average of 22 days. Researchers hope that this "smart" immune response to drug release strategies will be extended to clinical use as soon as possible.
The first author of the paper is Dr. Wu Jindao of Nanjing Medical University and Zheng Zhen, a doctoral student at the School of Chemistry and Materials Science of China University of Science and Technology. Liang Gaolin is the last author of the communication.
The project was funded by the National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars and the Innovation Group Project of the Fund Committee.
Source: University of Science and Technology of China
Easily assembled, eco friendly tent greenhouses garden grow mini type and feature
No tool required!
1.Ideal for propagating seeds,growing plants&vegetables.
2.Roll-up zipped front panel for easy access.
3.Protect plants from too much heat or cold,shield plants from dust and gale and keep out pests.
4.Includes guy ropes&ground pegs for extra stability
5.The cover is renforce PE interwoven cover.
6.The frame is rust proof and galvanised.
7.Easy to assemble!
8.UV stabilised
Garden Greenhouse,Mini Garden Greenhouse,Green Garden Greenhouse,Poly Garden Greenhouse
JIANGSU SKYPLAN GREENHOUSE TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , https://www.alibabagreenhouse.com