Release date: 2016-06-21
The Jiang Tianzi team of the Brain Network Research Center of the Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with other teams at home and abroad, succeeded in drawing a new human brain map through a six-year effort: brain network group map. The map includes 246 sub-regions of fine brain regions and multi-modal connection patterns in the sub-intervals of brain regions. It has broken through the idea of ​​traditional brain mapping for more than 100 years, and introduced brain structure and functional connection information to finely divide brain regions and brains. The new ideas and methods of map mapping are 4-5 times finer than the traditional Brodmann maps, with objective and accurate boundary positioning. For the first time, a living whole brain connection map on the macro scale is established. Since 2011, some of the results of this systematic research work have been published in famous journals such as Journal of Neuroscience, Cerebral Cortex, and Human Brain Mapping, with more than 20 articles. Recently, the whole brain fine-area map and its whole brain connection map were published online on the Cerebral Cortex (titled: The Human Brainnetome Atlas: A New Brain Atlas Based on Connectional Architecture), which has attracted wide attention from the international academic community.
The human brain map is the cornerstone for understanding the structure and function of the brain. The development of the brain map is driven by factors such as the development of brain science itself and major breakthroughs in neurotechnology, and has experienced different historical stages. At present, the most commonly used brain map is the brain map of German neuroscientist Brodmann who used cell construction on a single human cadaver tissue specimen more than 100 years ago, that is, the Brodmann map, although some foreign laboratories tried to use ultra-thin sectioning technology, dyeing technology and display. Micro-observation technology, based on ultra-thin sections of brain specimens to construct a probabilistic brain map, hopes to refine the Brodmann partition to a certain extent, but because it can not be divided into specific individuals, it is time-consuming and labor-intensive, and its application is somewhat restricted.
In the past 30 years, a group of imaging technologies represented by non-invasive magnetic resonance technology can image the spatial and temporal resolution of the human brain in an unprecedented and non-invasive way. It can measure the shape and size of the brain, and connect different regions of the brain. The nerve fibers, as well as changes in the functional activities of different circuits or pathways in the brain, and so on. Using magnetic resonance imaging technology to obtain large images of living brain images, the brain structure and functional areas can be finely divided and brain maps suitable for living individuals can be produced. At present, although there are some brain maps based on magnetic resonance image reconstruction, they are basically based on structural magnetic resonance imaging. The brain region is mainly based on the groove back topology distribution, and the brain region definition is very rough, and even there are obvious errors. Difficult to correspond to the functional anatomy of the brain.
The Brain Network Group Research Center of the Institute of Automation breaks through the bottleneck of traditional brain mapping, and puts forward the idea of ​​using brain structure and function connection information to draw the brain network group map. Since 2010, the team has been funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Strategic Science and Technology Specialist of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. The mapping methods and functional verification of the brain network group maps by a number of comprehensive hospitals and research institutes in the United Nations. Conduct a systematic study and conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the tools and software required for the brain network group map. The brain network group map has been openly shared on its portal (http://atlas.brainnetome.org) and is available free of charge to researchers and clinicians in relevant research fields at home and abroad by means of online display and software download.
At present, the brain network group map has attracted great attention from domestic and foreign counterparts. For example, the Human Brain Project (HBP) will soon release the map on its Neuroinformatics Platform (NIP), international neuroinformatics coordination. The International Neuroinformatics Coordinating Facility (INCF) has published the Human Brain Network Group Map (https://scalablebrainatlas.incf.org/human/BNA) online the first time. In addition, some internationally renowned neuroimaging software platforms, such as SPM, FSL, etc., provide the brain network group map as the main human brain map for users to use.
The brain network group map not only contains the fine cerebral cortex brain region and subcortical nucleus sub-region structure, but also quantitatively depicts the anatomical and functional connection patterns of different brain regions, and detailed each sub-region. Functional description. The construction of brain network group map will lead the future development of human brain map from specimen to living body, from rough to fine, from a single anatomical description to integrated description of integrated structure, function and connection mode, in order to realize brain science And provide the basis for innovation at the source of brain disease research. The brain network group map can provide the structural and functional connection patterns of each sub-region, thus clarifying the organizational mode and functional significance of each sub-region, which provides an indispensable tool for studying the relationship between brain and behavior on a macro scale. It will deepen the understanding of human mental and psychological activities, open up new ways for understanding the structure and function of human brain, and provide important enlightenment for the design of future brain-like intelligent systems. In addition, the brain network group map can provide individualized sub-regions of fine brain regions and quantitative connection patterns, which not only provide accurate localization for new therapeutic techniques for neurological and psychiatric diseases, but also for areas with brain stroke damage and epilepsy lesions. The positioning, the precise resection of gliomas in neurosurgery, and the more rigorous and effective protection of functional brain regions, can greatly promote the application of such techniques in the treatment of clinical neuropsychiatric diseases, and improve Diagnostic quality and therapeutic effect.
Brain network group map is the inevitable trend of human brain map development and neurotechnology advancement. It is the key to breakthroughs in related disciplines such as brain science, cognitive science, and cognitive psychology. It can be used to analyze neural circuits of neurological and psychiatric diseases. Abnormal structure and function, and lay a solid foundation for the development of a new generation of diagnostic and therapeutic techniques.
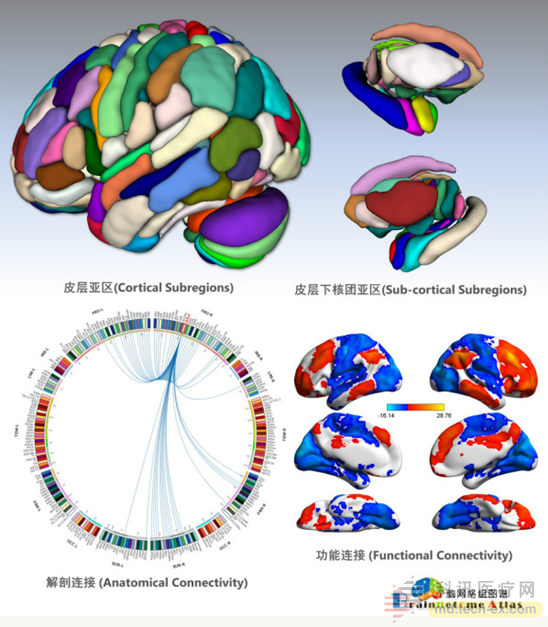
Human brain network group map: including 246 sub-regions of fine brain regions, and multimodal connection patterns in subregions of brain regions
Source: Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Interventional Accessories,Introducer Sheath,Introducer Sheath Kit,arterial sheath introducer
Anesthesia Medical Co., Ltd. , https://www.medicaldiverse.com