Key words
Gas chromatography; milk; amitraz; 2,4-dimethylaniline
aims
Establish an efficient method for the determination of metformin and its metabolites in milk. The amylose and its metabolites in milk are hydrolyzed to 2,4-dimethylaniline under acidic conditions. After the extraction of the alkane, after derivatization, the detection limit of the gas chromatograph analytical method is far below the maximum residue limit of the ampoule specified in the national food safety standard of 0.05mg/kg.

introduction
Amitraz is a broad-spectrum acaricide that has been used extensively at home and abroad. It has been found that its metabolite 2,4-dimethylaniline is carcinogenic and that metformin can pass through the food chain. Transmission, inhalation, ingestion or absorption through the skin can cause poisoning, posing a potential cancer risk to the human body [1]. Therefore, the “Safety Regulations for the Use of Pesticides†issued by the Ministry of Agriculture and the Ministry of Health of China lists it as a highly toxic acaricide, which is clearly prohibited from being used, and its use is also prohibited by CAC and EU.
At present, the determination method of the residual ampoule is gas chromatography and liquid chromatography [2-5]. The direct determination of the parenteral content of the methotrexate by liquid chromatography neglects the property of the diformin to be decomposed into 2,4-dimethylaniline under acidic conditions, and only the parenteral content of the metformin is determined as the amitraz. The total residue is unscientific. In the new national food safety standard issued in 2014, GB29707-2013 "Food Safety National Standard for Determination of Residues of Residual Markers in Milk in Milk" is the determination of amitraz and its metabolites in milk by gas chromatography. Residual amount.
The method is improved on the basis of the standard method, and the carbamazepine in milk is hydrolyzed to 2,4-dimethylaniline under acidic conditions, derivatized with heptafluorobutyric anhydride, and quantified by gas chromatography. Total residual amount of amitraz and its metabolites. The method is simple to operate, and the detection limit is far lower than the maximum residue limit of 0.05 mg/kg of amitraz as specified in the national food safety standard.
instrument
Trace1310 gas chromatograph with ECD detector (Thermo Scientific);
AS1310 Autosampler (Thermo Scientific)
Constant temperature drying chamber centrifuge balance vortex mixer
Consumables
Column: TG-5MS (30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm) (Thermo Scientific, PN: 26098-1420)
Reagents and standards
Amitraz standard: content ≥ 99%; 2,4-dimethylaniline standard: content ≥ 95%
Sodium hydroxide: excellent grade pure; hydrochloric acid: excellent grade pure; anhydrous sodium sulfate: excellent grade pure, used after 450 ° C burning; sodium bicarbonate: excellent grade pure; n-hexane: chromatographic purity
1mol/L hydrochloric acid solution: Take 8.3mL of concentrated hydrochloric acid, dilute to 100mL with water.
4mol/L sodium hydroxide solution: Weigh 16g of sodium hydroxide, dissolve it with water and dilute to 100mL
Saturated sodium bicarbonate solution: Weigh 9.6 g of sodium bicarbonate, dissolved in 100 mL of water
Preparation of standard solution
Stock solution: Accurately weigh 10.0mg of diammonium and 2,4-dimethylaniline standards, dilute with n-hexane and dilute to 100mL, to obtain 100mg / L standard stock solution, stored in the refrigerator for use.
Standard intermediate solution: 1 mL of diammonium and 2,4-dimethylaniline stock solution were separately taken and diluted to 100 mL with n-hexane to obtain a standard intermediate solution with a concentration of 1 mg/L.
Sample preparation
Weigh 5.0 g of milk sample into a 50 mL centrifuge tube, add 10 mL of 1 mol/L hydrochloric acid solution, let stand in a constant temperature oven at 60 ° C for 30 min, cool, centrifuge at 10,000 rpm for 10 min, take the supernatant in another centrifuge tube, add 4 mol. /L Sodium hydroxide solution 10mL, n-hexane 5mL, vortex to mix, let stand for 5min, centrifuge at 10000rpm for 10min, take 2mL of the upper layer of n-hexane solution for 90min, during which the ultrasound is taken out every 30min for 5min. After derivatization, let stand for 10 min, add 2 mL of saturated sodium bicarbonate solution, mix well, take the organic phase layer, add 1 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate to remove water, and measure by gas chromatography.
Experimental condition
Column: TG-5MS (30 m × 0.25 mm × 0.25 μm);
Column temperature: 50 ° C (1 min), 10 ° C / min to 250 ° C (5 min);
Injection mode: splitless injection, no split time 1min; injection volume: 1 μL;
Inlet temperature: 260 ° C;
Carrier gas: high purity nitrogen (99.999%), constant current mode, 1 mL/min;
Detector temperature: 300 ° C, makeup gas, nitrogen, 15 mL / min.
Results and discussion
Optimization of pretreatment conditions: Amitraz is hydrolyzed faster under acidic conditions and hydrolyzed more thoroughly. Hydrolyzed 2,4-dimethylaniline is a basic compound, which is salted with acid under acidic conditions and soluble in water. Under alkaline conditions, soluble in most organic solvents. Therefore, after hydrolysis, an alkaline solution was added and then n-hexane was added for extraction. The n-hexane extract was derivatized with heptafluorobutyric anhydride to give 2,4-dimethylphenyl heptafluorobutyramide.
Under the selected chromatographic conditions, the chromatogram after derivatization of the standard is shown in another centrifuge tube of Figure 1. Add 10 μL of heptafluorobutyric anhydride, mix well, and maintain a constant linear relationship at 60 ° C and measure the lower limit: Accurately remove 2 The appropriate amount of 4-dimethylaniline standard intermediate solution was diluted with n-hexane to prepare standard working solutions with concentrations of 0, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100 μg/L, each taking 2.0 mL, and treated according to the derivatization step. For gas chromatography. Taking the peak area as the ordinate, the corresponding standard solution concentration as the abscissa, and drawing the standard curve as shown in Fig. 2. The detection limit of the method was calculated by 3 times the signal-to-noise ratio. The lower limit of the method was 2 μg/kg.
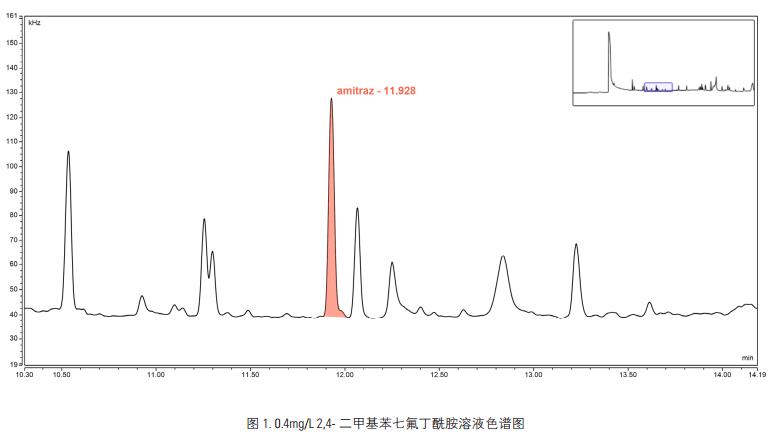
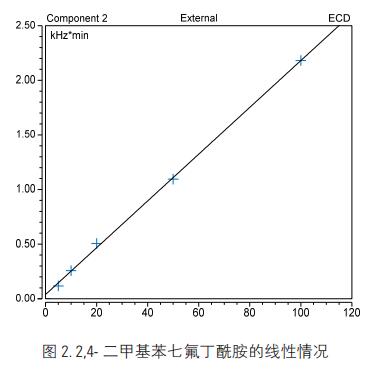

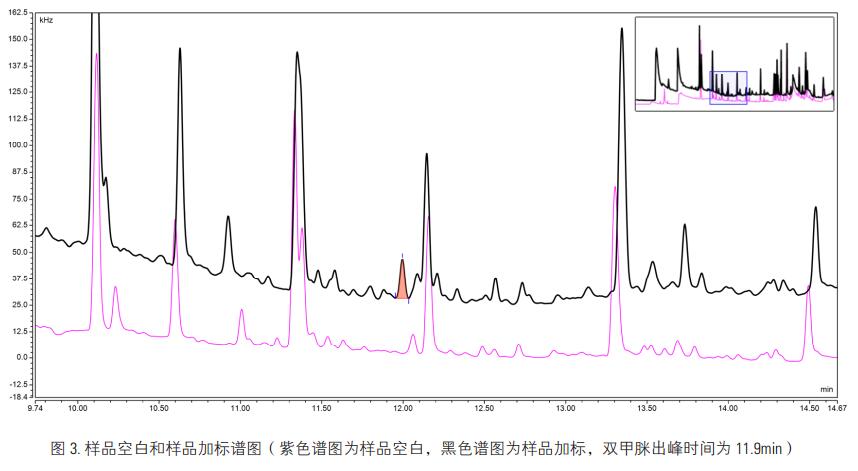
Â
in conclusion
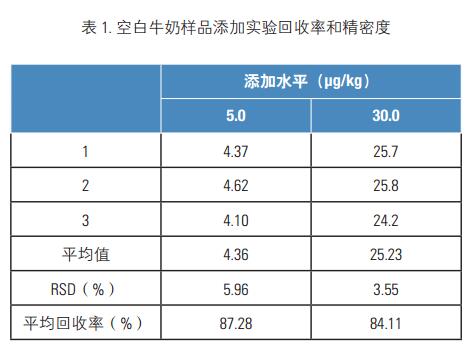
The metformin in the sample was hydrolyzed to 2,4-dimethylaniline under acidic conditions. After alkalization, it was extracted with n-hexane. After derivatization, it was detected by Thermo Fisher's new gas chromatograph and quantified by external standard method. The results showed that the average recovery of amitraz was 84.1-87.3%, the RSD value of 3 parallel determinations was ≤5.96%, and the lower limit of the method was 2ng/g. This method is simple, scientific and accurate, and has high sensitivity. It can meet the residue analysis requirements of metformin in milk.
references
[1] Wu Jianming, Liang Shuhua, Zhang Yunying et al. Toxicity study of amitraz. Chemical Labor Protection, 1992, 13(3): 134-135
[2] Zheng Yongquan, Yao Jianren, Shao Xiangdong et al. Method for determination of residual metformin in honey. Pesticide Science and Management, 2000, 21(3): 14-16
[3] Zhao Zengyun, Wu Bin, Shen Chongxi et al. Determination of the retention of metformin in honey by high performance liquid chromatography. Chinese Beekeeping, 2005, 56(5): 4-5
[4] Wang Yuanhong, Rong Hui, Zhang Ying et al. Determination of the residual amylose in food by gas chromatography. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene, 2001, 13(6): 20-22
[5] Yang Rong. Determination of trace amitraz in tea by gas chromatography. Food Science and Technology, 2006, 2: 94-95
During plant growth, a series of metabolic and biochemical processes are carried out, forming and accumulating various chemical substances, which constitute the chemical composition of plants. Plant extracts are very complex, and there are many types of chemical components, and the components of different parts are different. General plants contain the following types of chemical components: alkaloids, glycosides, organic acids, resins (including resin acids, resin alcohols and resin hydrocarbons), volatile oils, sugars (including starch, inulin, gums and mucilage, etc.) , amino acids, proteins and enzymes, tannins, plant pigments (including chlorophyll, carotene, flavonoids, beta red bases and quinones, etc.), oils and waxes, and inorganic components (trace elements).
There are many kinds of plant extracts, and their main functions in skin medicines, curative cosmetics and cosmetics include: anti-irritant, anti-inflammatory, wound healing, anti-infection, sterilization, moisturizing, skin protection, etc. Whether it is a single Plant Extract or a compound extract, its efficacy is often various, especially the clinical efficacy of compound extract is reflected in the comprehensive effect and overall effect of compound compatibility, and its efficacy is sometimes more effective than separation and purification. The efficacy of the combination of ingredients is good.
Pure natural plant extract,Salvia Miltiorrhiza Seeds Extract,Eclipta Prosteata Extract Powder,Piperine,Piperine Extract,Damiana Extract
Xi'an Henrikang Biotech Co.,Ltd , https://www.xianhenrikangbio.com