Release date: 2018-03-16
Researchers from Rice University have found an interesting phenomenon. They have been studying the establishment of drug delivery systems through hydrogels, but they have surprisingly found that hydrogels are also very helpful for wound healing even without additional drugs.
The research team published an article in the journal Biomaterials to introduce this particular hydrogel. The self-assembled multidomain peptide (MDP) containing the amino acid sequence K2(SL)6K2 does have biological activity. This hydrogel is injected into the tissue and provides a growing environment for the newborn cells, which is gradually removed over a period of weeks.
Dr. Jeffrey Hartgerink, a researcher in chemical and biological engineering at Rice University, discovered that the synthetic scaffold that was originally developed for drug delivery itself is a good help for cell and blood vessel growth in new tissues.
Hydrogel subcutaneous implants can promote the growth of cells and blood vessels because the hydrogel is replaced by new tissue.
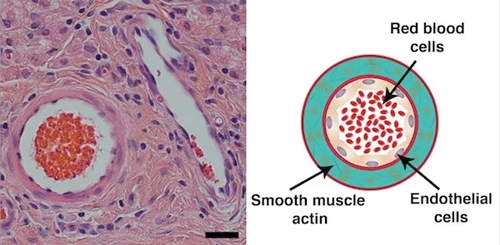
Image source: Rice University
Once, Hartgerink and his team members began to study this phenomenon. They found that even without additives, their MDP can be quickly infiltrated by host cells, causing a temporary inflammatory response, without forming fibrous vesicles, supporting mature vascular networks. Infiltrate and rebuild nerve fibers.
"We were surprised to find that this peptide we thought was a control had such a strong influence," Hartgerink said. "It has been shown that the inherent structure and chemical properties of this peptide, although very simple, have led to strong biological responses."
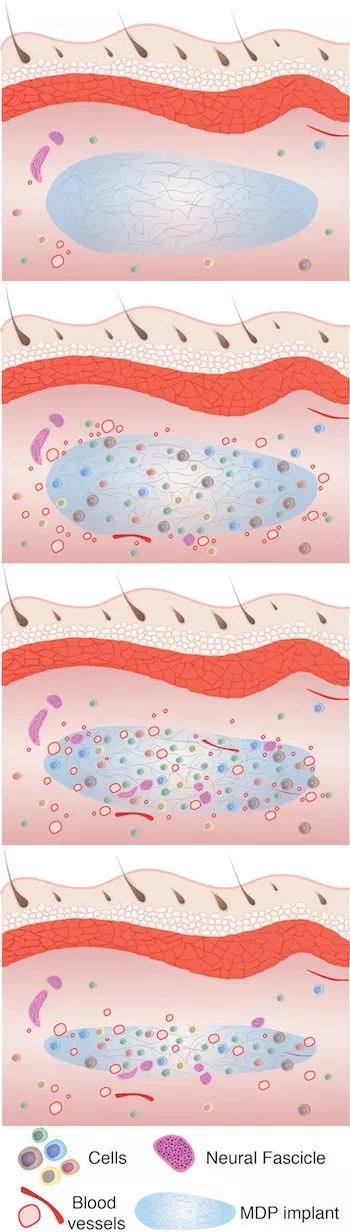
This schematic shows the changes that occur when the hydrogel is injected into the tissue for 6 weeks. From top to bottom, the process begins with cell infiltration, followed by vascularization, neurochemistry, and slow degradation of the hydrogel. Replaced by healthy organizations. Image source: Rice University
Researchers say that when foreign substances, such as gels, are injected into the system for natural inflammatory reactions, cells that pull secreted proteins are involved in cell infiltration, scaffold degradation, vascularization, and neuronalization. Tests showed a "statistically significant" increase in cytokines that caused an inflammatory response after hydrogel injection, just as an anti-inflammatory drug increased, and both conditions remained stable on the third day and lasted for two weeks. .
According to Hartgerink, this suggests that hydrogels seem to use the body's innate ability to heal because it transforms from a pro-inflammatory to a pro-healing environment.
He said: "We finally found out that this special peptide allows the body to heal itself and has a significant boost. We believe that the key step is the initial very rapid cell infiltration. Once these cells are in place, they will Produces an impressive regenerative response, including angiogenesis and neurogenesis."
Hartgerink said the lab is looking to apply the peptide to wound healing in diabetic ulcers. It is well known that the wound healing of diabetic patients has great difficulties, and in severe cases, it can cause serious consequences such as amputation. If this peptide hydrogel can help the wound healing of patients well, it will be a very valuable application direction.
Reference materials:
[1] Hydrogel helps heal without any
Source: Health New Vision
Erythritol For Jams,Making Jelly With Erythritol,Sweeteners With Erythritol,Natural Erythritol Sweetener
Ningxia Eppen Biotec CO.,LTD , https://www.nxeppen.com